
mathnstuff.com/math/precalc/MAT129fa25/p.3.htm
© 2025 A2, Agnes Azzolino
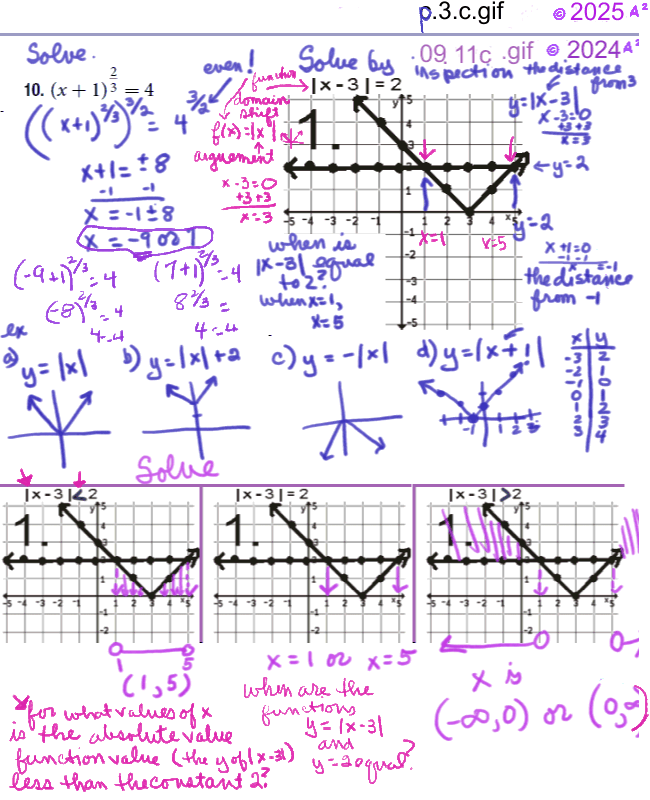
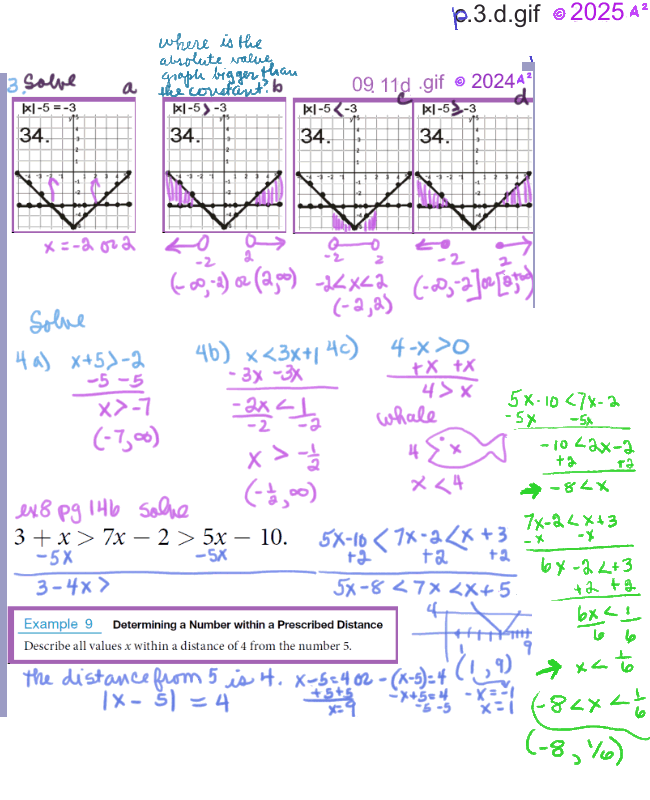
Solving Quadratic and Rational inequalities. Text 2.7, PG. 142
 |
mathnstuff.com/math/precalc/MAT129fa25/p.3.htm © 2025 A2, Agnes Azzolino Solving Quadratic and Rational inequalities. Text 2.7, PG. 142 |
|
|
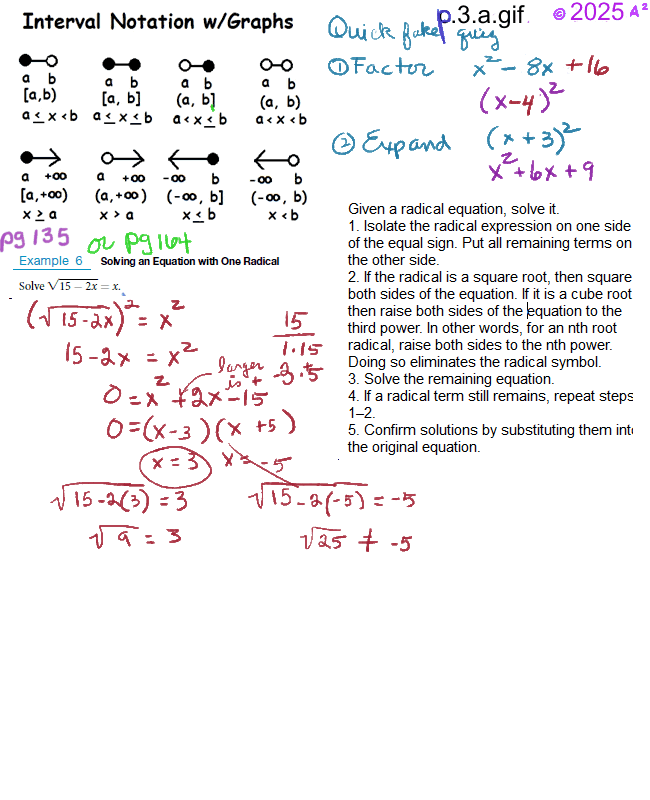
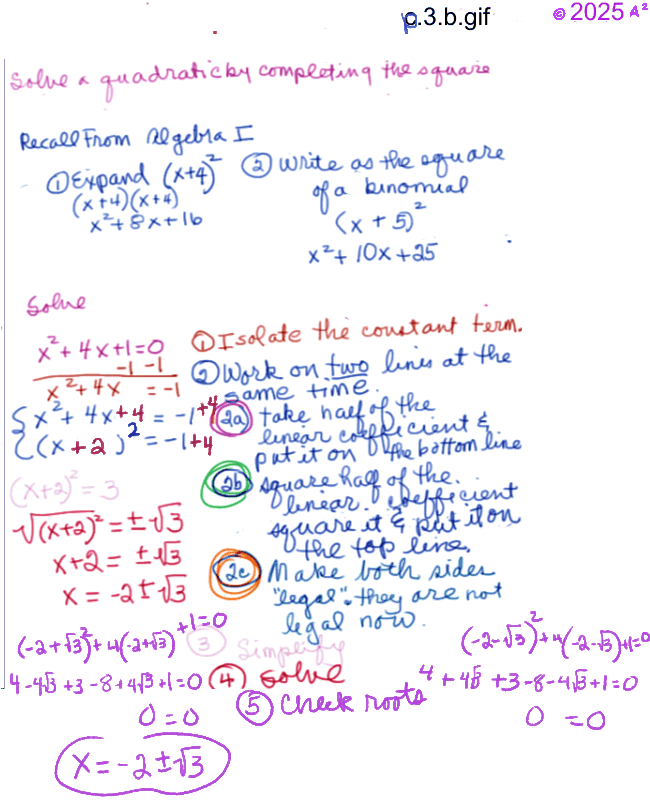
Quadratic Equation Solver is at the bottom of the page. See: 2.7, pg 142 in m129.ch2to4.1.fa24.pdf 2.7 - Linear Inequalities and Absolute Value Inequalities -- Solving Quadratic and Rational inequalities, pg. 142, Learning Objectives * Use interval notation. * Use properties of inequalities. * Solve inequalities in one variable algebraically. * Solve absolute value inequalities.

 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
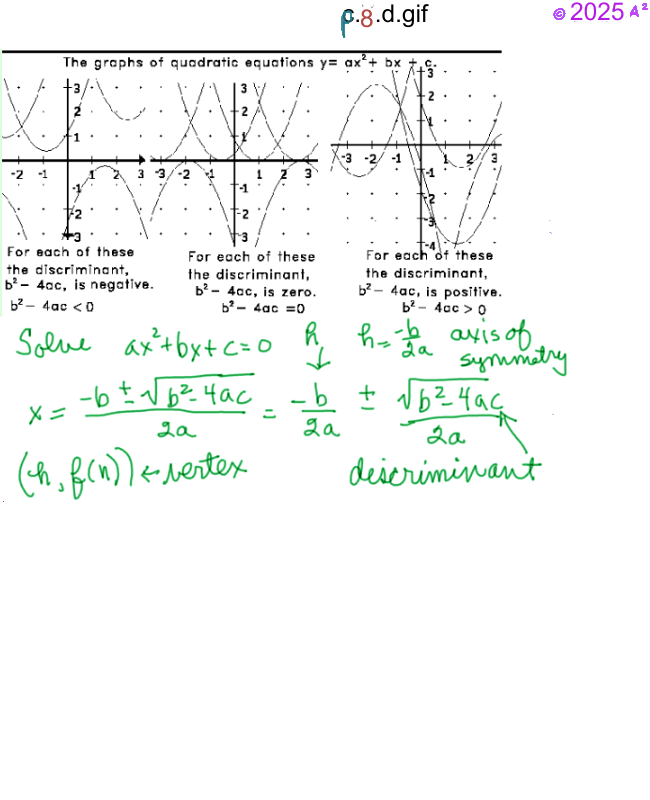
If ax² + bx + c = 0 then x =
| |
|
| |